動機
補完以前的記憶,下面會介紹
- 經典款: red-black tree
- 但在面試或是競賽馬上code出來應該有點難,所以通常用下面兩種
- rotation base: splay tree
- merge/split base: treap
red-black tree
只要符合下面兩個限制的tree就是red-black tree
- 紅的不會和紅的接在一起
- 雙紅矛盾
- 從根到任意leaf的路徑長度都一樣長
- 黑高矛盾 (不等高)
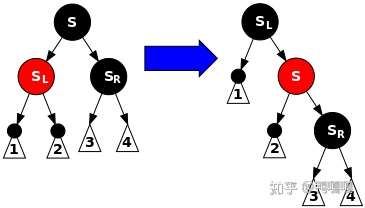
insert (雙紅矛盾)
insert如何不破壞兩個條件?
黑高矛盾: 每次都插入紅的 雙紅矛盾:
- 插入點是root,child有紅
- 把root換成黑
- 插入點是child (parent是黑的,並假設插在左邊)
- 左的child是紅的: 直接右旋
- 右的child是紅的: 左旋再右旋
插右邊的case? 這是對稱的,所以不列了
可以注意到,第2個case的所有case的結果都會是
- 根是紅的
- 像這種
/\形狀
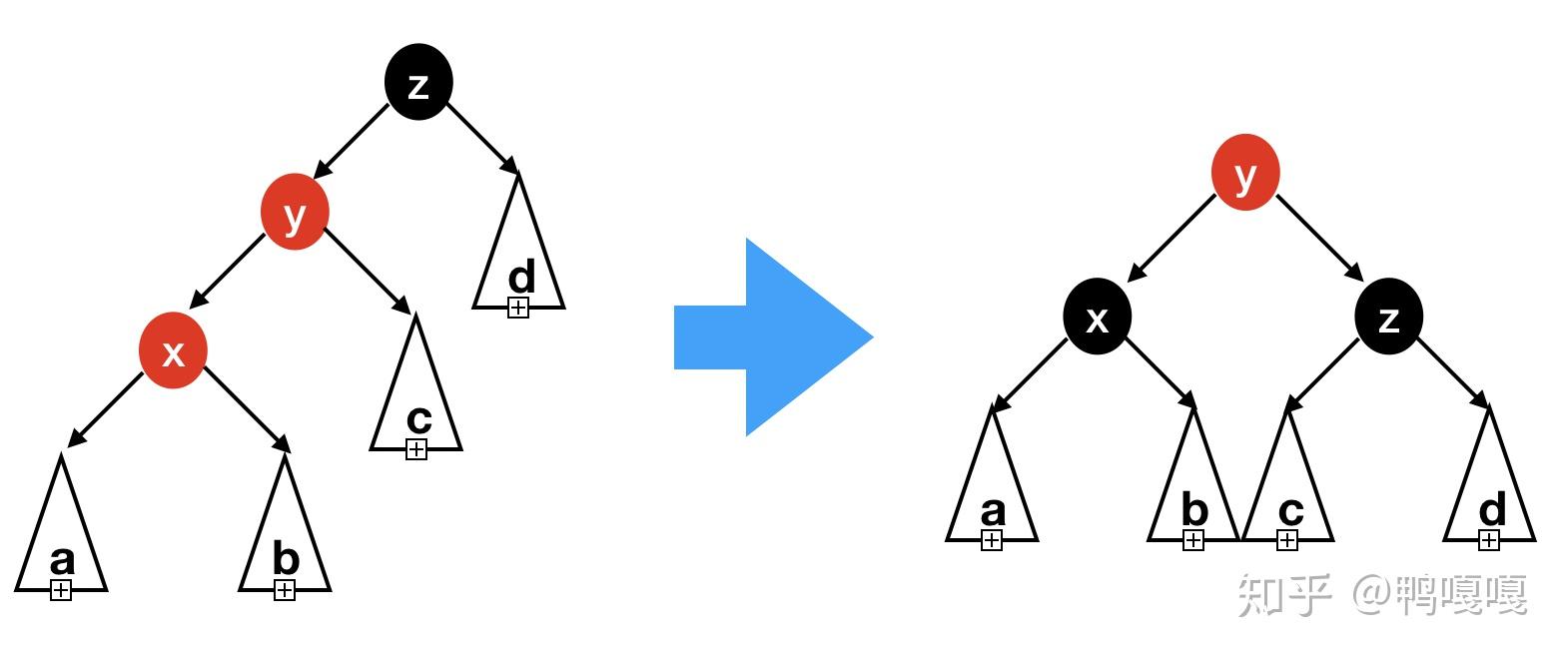
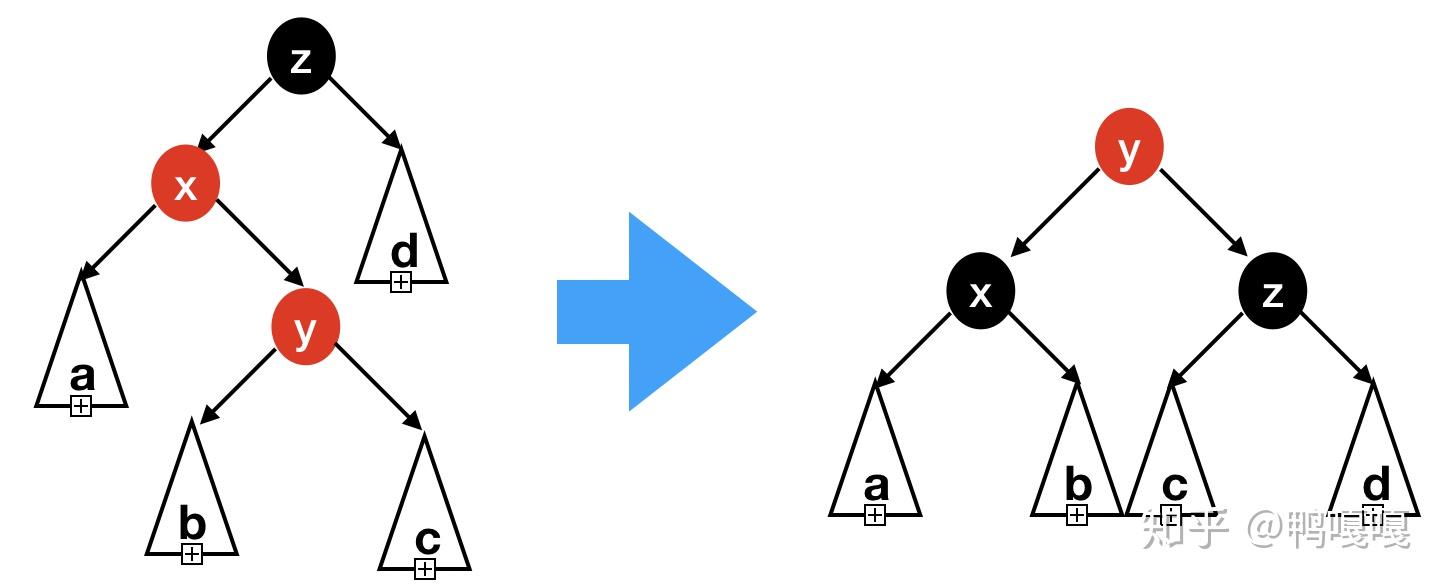
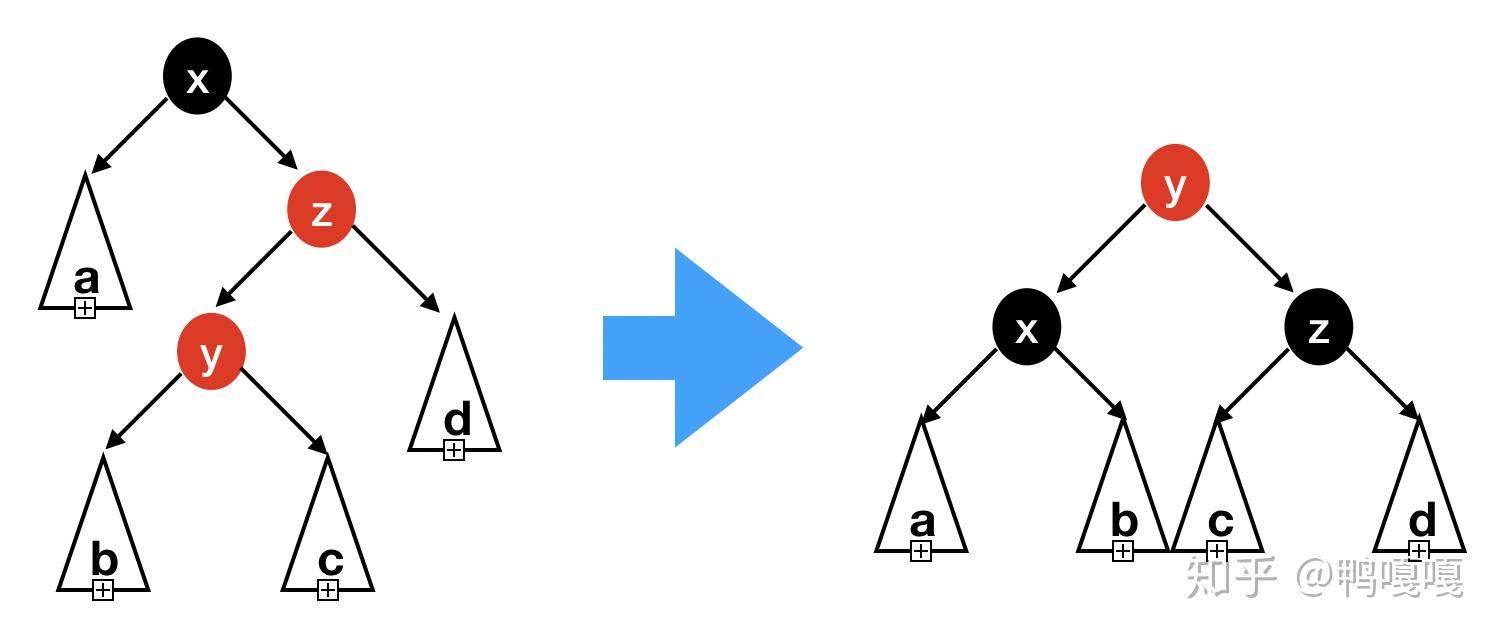
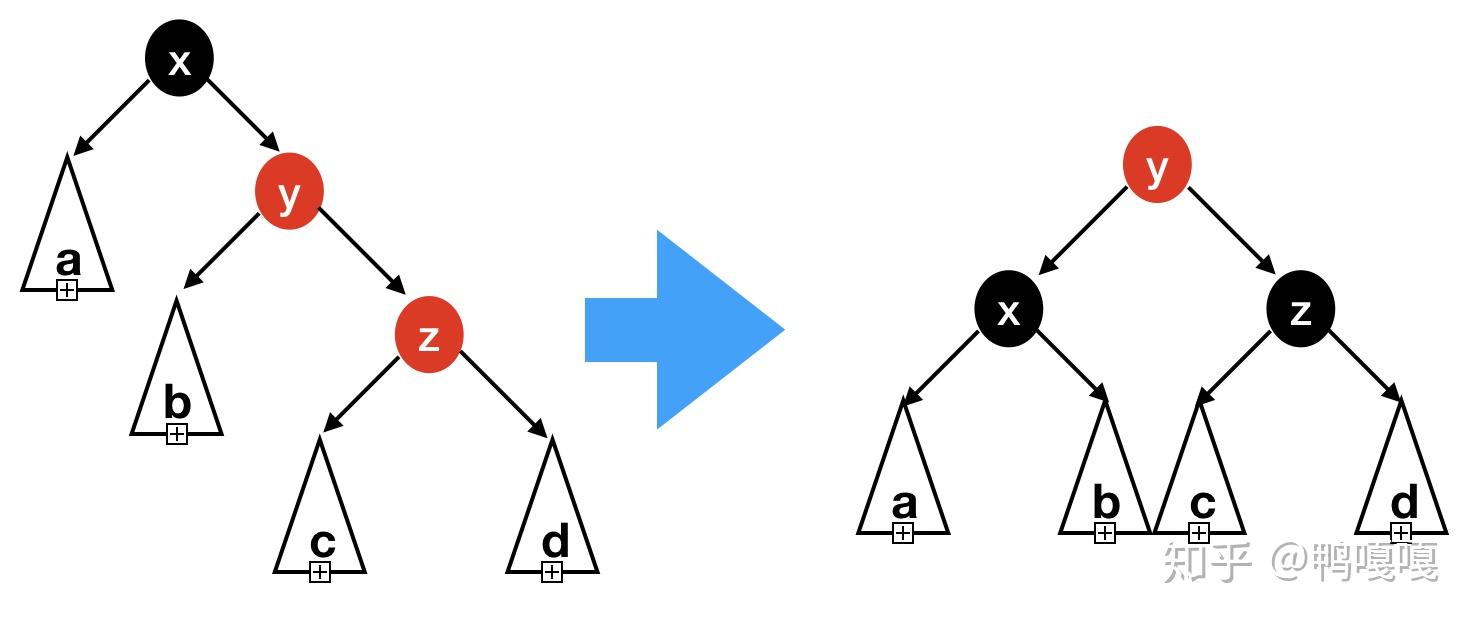
剛剛提到左旋與右旋,來完成再平衡,但是haskell可以直接build資料,所以…
blacken Nil = Nil
blacken (Node _ value left right) = Node Black value left right
insert x root = blacken $ insert' root
where insert' Nil = Node Red x Nil Nil
insert' root@(Node color y left right)
| x < y = balance color y (insert' left) right
| x > y = balance color y left (insert' right)
| otherwise = root
-- left-right
balance Black z (Node Red x a (Node Red y b c)) d = Node Red y (Node Black x a b) (Node Black z c d)
-- left-left
balance Black z (Node Red y (Node Red x a b) c) d = Node Red y (Node Black x a b) (Node Black z c d)
-- right-left
balance Black x a (Node Red y b (Node Red z c d)) = Node Red y (Node Black x a b) (Node Black z c d)
-- right-right
balance Black x a (Node Red z (Node Red y b c) d) = Node Red y (Node Black x a b) (Node Black z c d)
balance color value left right = Node color value left right
delete (黑高矛盾)
delete就是BST的delete
- 在leaf: 換成nil
- 只有一個child: 把唯一個child拉上去
- 兩個child: 右child最小的換上來,再把它刪掉
所以現在重點是換下去的那個點怎麼刪
刪的是
- 紅的: 沒事
- 黑的: 數量可能不對 (黑高矛盾)
(把紅的看成收束下面的兩個child成一條長度,因為兩邊的長度一樣) (紅的可以輕易變成黑的,但黑的不行直接變成紅的) 要刪的是黑的,所以可以從parent與neighbor的顏色生出4種case
| root: red | root: black | |
|---|---|---|
| neighbor: red | impossible | 左旋,原本的parent變紅 |
| neighbor: black | 原本的parent變黑,neighbor變紅 | neighbor變紅 |
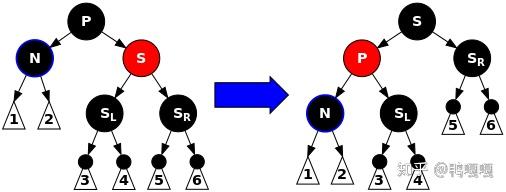
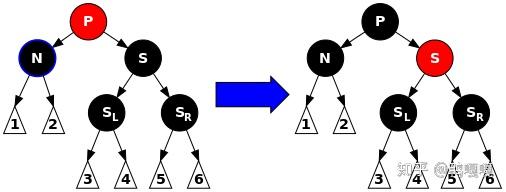
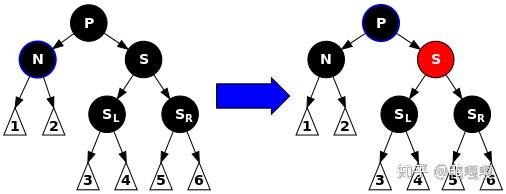
neighbor變紅,不會觸發雙紅矛盾? 有可能,如果兩個child都是黑的就沒事,其中一個是紅的就要處理了
只有右邊是紅、兩個紅: 左旋 (把長度補回去),把紅的標成黑
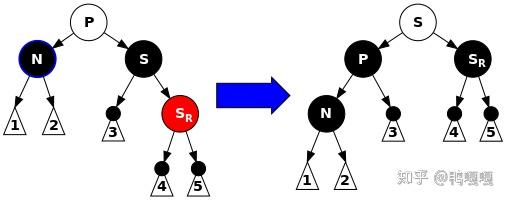 只有左邊是紅: 先左旋,轉成一條就可以用前面的方法了
只有左邊是紅: 先左旋,轉成一條就可以用前面的方法了
isBlack (Node Red _ _ _) = False
isBlack _ = True
balL color y (left, True) right = (Node color y left right, True)
balL color y (left, False) right = balL' color y left right
balL' color1 p n (Node color2 s sl sr)
-- neighbor: red, root: black
| color2 == Red = balL Black s (balL' Red p n sl) sr
-- neighbor: black, root: black OR red
| isBlack sl && isBlack sr = (Node Black p n (Node Red s sl sr), color1 == Red)
-- 只有右邊是紅、兩個紅
| not (isBlack sr) = (Node color1 s (Node Black p n sl) (blacken sr), True)
-- 只有左邊是紅
| otherwise = let (Node Red x sll slr) = sl in balL' color1 p n (Node Black x sll (Node Red s slr sr))
把剩下的列完
findMin (Node _ x Nil _) = x
findMin (Node _ _ left _) = findMin left
balR color y left (right, True) = (Node color y left right, True)
balR color y left (right, False) = balR' color y left right
balR' color1 p (Node color2 s sl sr) n
| color2 == Red = balR Black s sl (balR' Red p sr n)
| isBlack sl && isBlack sr = (Node Black p (Node Red s sl sr) n, color1 == Red)
| not (isBlack sl) = (Node color1 s (blacken sl) (Node Black p sr n), True)
| otherwise = let (Node Red x srl srr) = sr in balR' color1 p (Node Black x (Node Red s sl srl) srr) n
delete x t = fst $ delete' x t
where delete' x Nil = (Nil, True)
delete' x root@(Node color y left right)
| x < y = balL color y (delete' x left) right
| x > y = balR color y left (delete' x right)
| otherwise = deleteRoot root
deleteRoot (Node color _ Nil Nil) = (Nil, color == Red)
deleteRoot (Node _ _ left Nil) = (blacken left, True)
deleteRoot (Node _ _ Nil right) = (blacken right, True)
deleteRoot (Node color _ left right) = let m = findMin right in balR color m left (delete' m right)
Ref 有人能讲清楚《Algorithms》中左倾红黑树(LLRB)删除操作的每一行代码吗?
splay tree
利用特別的旋轉(splay),把最近存取的點轉到root,達成所有操作均攤log n
如果只有父節點,也就是父節點是root,就直接rotate 但如果有祖父節點時要做下面兩個case的旋轉

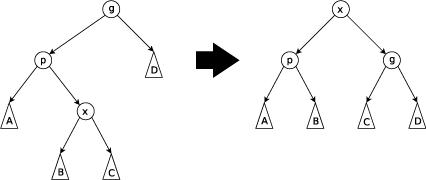
Q: 為什麼這個rotate這麼特別,如果說只是轉上去,其實不用管祖父節點? A: 這樣才能確保出來的深度是最小的
P.S.: C++的rotate很複雜,因為一次只能assign一次,所以狀態一直變,但是利用平行賦值就好很多
每次改node,都要確認被改過的node的left, right, parent都是對的!!
class Node:
def __init__(self, key:int = 0, parent = None, left = None, right = None):
self.key, self.parent, self.left, self.right = key, paretn, left, right
def left_rotate(self):
oldroot, newroot = self, self.left
newroot.parent, oldroot.parent = oldroot.parent, newroot
newroot.right, oldroot.left = oldroot, newroot.right
if newroot.left:
newroot.left.parent = oldroot
if newroot.parent:
if newroot.parent.left is oldroot:
newroot.parent.left = newroot
else:
newroot.parent.right = newroot
def right_rotate(self):
oldroot, newroot = self, self.right
newroot.parent, oldroot.parent = oldroot.parent, newroot
newroot.left, oldroot.right = oldroot, newroot.right
if newroot.right:
newroot.right.parent = oldroot
if newroot.parent:
if newroot.parent.left is oldroot:
newroot.parent.left = newroot
else:
newroot.parent.right = newroot
def is_left(self, other):
return self.left is other
def splay(self):
while self.parent:
parent, grand_parent = self.parent, self.parent.parent
if grand_parent:
if grand_parent.is_left(self.parent):
if left_child:
grand_parent.left_rotation()
parent.left_rotation()
else:
parent.right_rotation()
grand_parent.left_rotation()
else:
if not left_child: # is right child
grand_parent.right_rotation()
parent.right_rotation()
else:
parent.left_rotation()
grand_parent.right_rotation()
else:
# zig
if parent.left is self:
parent.left_rotate()
else:
parent.right_rotate()
def find(self, key: int) -> Node:
ret = None
if self.key == key:
ret = self
elif self.right and self.key < key:
ret = self.right.find(key)
elif self.left and self.key > key:
ret = self.left.find(key)
return ret
def find_min(self):
return self.left.find_min() if self.left else self.key
insert與BST差不多,但是最後要splay!!
def insert(root: Node, key: int):
## WTF
prev: Node, now: Node = None, root
while now:
prev, now = now, now.right if now.key < key else now.left
now = Node(key, prev)
if prev.key < now.key:
prev.right = now
else:
prev.left = now
now.splay()
基本就是BST的remove,但要先把target splay,再做BST的remove
def remove(root, key):
## WTF
target: Node = root.find(key)
def take_place(a, b):
if b:
b.parent = a.parent
if a.parent:
if a.parent.left is a:
a.parent.left = b
else:
a.parent.right = b
if target:
target.splay()
if not target.left:
take_place(target, target.right)
elif not target.right:
take_place(target, target.left)
else:
miniumum = target.right.find_min()
if miniumum.parent is not target:
take_place(miniumum, miniumum.right)
miniumum.right = target.right
miniumum.right.parent = miniumum
take_place(target, miniumum)
miniumum.left = target.left
del target
treap
每個點都有
- key: BST的val
- pri: heap的比較數字 所以叫tree + heap = treap
在維持heap的前提下(意思是heap先滿足),滿足BST的需求
同時treap有以下性質
- 給定 n 個節點的 key、pri 的大小關係,那麼這棵 treap 的形狀唯一。
- 給定 n 個節點的 key,在 n 個節點的 pri 都隨機的前提下(也就是 treap 的形狀隨 機),任一個選定的節點的期望深度為 O(log n)。
所以根據第2點,我們pri要是random
class Node:
def __init__(self, key: int = 0, left = None, right = None):
self.left, self.right = left, right
self.key, self.pri = key, random()
def inspect(self) -> [int]:
ret = [self.key]
ret += self.left.inspect() if self.left else []
ret += self.right.inspect() if self.right else []
return ret
def size(self) -> int:
ret = 1
ret += self.left.size() if self.left else 0
ret += self.right.size() if self.right else 0
return ret
有rotate的寫法,但很複雜,同時有merge/split的寫法,好寫很多,所以做merge/split
split: 把一顆樹根据數字分成左右兩顆treap
- root key比較小就跟左邊、比較大就跟右邊,剩下的(另一側)拿去遞迴,繼續割 merge: 依據pri與key合併兩棵treap
- 同時限制左邊的treap的所有key都小於右邊的treap
- 只要是合併split後的treap就可以滿足這個限制
- merge/split互為反函數
def split(root: Node, key: int) -> [Node, Node]:
if not root:
return [None, None]
elif root.key <= key:
# 保留 root.left
# 繼續分 root.right,之後接上新的treap
l, r = split(root.right, key)
root.right = l
return [root, r]
else:
l, r = split(root.left, key)
root.left = r
return [l, root]
def merge(l: Node, r: Node) -> Node:
if not l or not r:
return l or r
elif l.pri > r.pri:
l.right = merge(l.right, r)
return l # 讓pri大的當root
else:
r.left = merge(l, r.left)
return r # 讓pri大的當root
insert:
- 基本上就是BST insert,但是還有pri!!
- 所以可以先看pri,如果比較大就插這裡 (用split生左右tree!!)
def insert(root: Node, target: Node):
if not root:
return target
elif target.pri > root.pri:
target.left, target.right = split(root, target.key)
return target
else:
# usual BST insert
if root.key <= target.key:
return insert(root.right, target)
else:
return insert(root.left, target)
remove:
- 遠比BST的remove簡單!!
- 遇到要刪的,直接merge原有的左右tree!!
def remove(root: Node, key: int) -> Node:
if not root:
return None
elif root.key == key:
return merge(root.left, root.right)
else:
if root.key <= key:
root.right = remove(root.right, key)
else:
root.left = remove(root.left, key)
return root
這個是set的union,作法就是用最大pri的treap作主軸,一直split右邊的treap,之後就是繼續unite被split出來的treap
def unite(l: Node, r: Node) -> Node:
if not l or not r:
return l or r
elif l.pri < r.pri:
return unite(r, l)
else:
r_left, r_right = split(r, l.key)
l.left = unite(l.left, r_left)
l.right = unite(l.right, r_right)
return l