動機
我之前學的DB根本就是假的 這是來自nthu的DB課程,有slide但沒有prjects
難道之後要跑CMU 15-445嗎? 不過有一說一,DB越看與xv6的fs真的很像,除了沒有SQL的部分
Why not file systems?
- query可以組合
- 以tx為單位
- ACID!!
- 有辦法recover
- 讓recover的資料一致
query怎麼處理?
SELECT p.id, p.text
FROM posts AS p, users AS u
WHERE u.id = p.authorId
AND u.name='Bob'
AND p.text ILIKE '%db%';
Query Optimization: plan

EXPLAIN
EXPLAIN ANALYZE -- show plan tree
SELECT *
FROM users
WHERE id<5 AND name ILIKE '%User%'
ORDER BY id DESC
LIMIT 2;
filter, zip, select (where, join, select)
FROM posts AS p, users AS u

WHERE u.id = p.authorId AND u.name=‘Bob’ AND p.text ILIKE ‘%db%’

SELECT p.id, p.text

Handling “Big” Data

when deleting
- NO ACTION (default): user not deleted, error raised
- CASCADE: user and all referencing posts deleted
Query Optimization: index

- index
- 一個mapping function
- 加速 equality 或是 range selections
- equality
- hashing function
- key到一堆有關的值
- 其他hash function的issue去看資料結構
- hashing function
- range selections
- B-Tree

- 最後map到一堆有關的值
- 每一個node就是放起點的list
- how to lock?
- Lock Crabbing Protocol
- Lock Crabbing Protocol
- B-Tree
- equality
- Input: field values or ranges
- search key
- Primary index vs. secondary index
- index中有沒有Primary key
- Primary index vs. secondary index
- search key
- Output: rids (record的id)
- 加速 equality 或是 range selections
- 因為是根據field建tree或hash,所以如果有改row,就要更新index
- Faster reads at the cost of slower writes
- 一個mapping function
inverted index

concurency
說好的ACID
- Atomicity: all or nothing
- 通常只有這個
- Consistent: db的整體狀態是對的
- Isolation: 這才是我印象中的atomic
- 要自己來
- Duration: 資料庫內的資料不會因為斷電,系統崩潰而損失資料。
總的來說,tx根本就是一般function (但會rollback)
怎麼出事
- Dirty Read: 有人讀還沒commit的欄位
- 如果之後這個欄位被rollback…
- 可能好: 最後有被commited
- 不好: 被rollback,之前看的資料就沒效了

- Non Repeatable read: (在tx中) 讀同個row兩次的結果不一樣 (race condition)
- row為單位的race condition

- Phantom Read: (在tx中) 同個query拿到的rows不一樣 (race condition)
- table為單位的race condition (在條件上race condition)

- Serialization Anomaly: 因為tx commit的順序不同導致最後結果inconsistence
- reorder
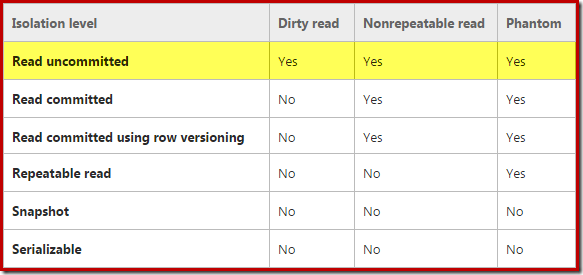
Isolation
- Read Uncommitted: 沒有任何保證
- Read Committed: 寫完的不會變了 (mem consistency)
- 可以用read lock與write lock來保證
- 鎖在tx的執行啟動與完成 (mutual exclusion)
- 可以用read lock與write lock來保證
- Repeatable Read: (就是名字寫的)
- 可以用read lock與write lock來保證
- 鎖在有用到的所有row
- 可以用read lock與write lock來保證
- Serialisable: tx跑起來與serial一樣
- dependency (mem barrier)
工具
- lock
- Pessimistic (Exclusive): mutex
- Optimistic (Shared): read/write lock 或是 seq lock
- snapshot:
- row versioning(MVCC): 就是row的持久化,每一個tx的更新對row來說都是一個版本的更新
- Two Phase Locking:
- 先把lock全部拿完,開跑
- 到最後再把lock還回去


Ref
How does a database server handle thousands of concurrent requests? On Concurrency Control in Databases
DB Architecture

Server and infrastructures (jdbc, sql, tx, and utils)
- Transaction
- Concurrency
- 2PC lock protocol
- 要用就先拿lock,用完馬上unlock
- strict 2PC lock protocol
- 一次拿完所有需要的lock,tx完成後unlock
- Multiple-Granularity Locks: allows users to set locks on objects that contain other objects
- 2PC lock protocol
- Recovery
- 定義Failure
- Transaction hangs
- System hangs/crashes
- Assumptions
- Contents in nonvolatile storage are not corrupted
- No Byzantine failure (zombies)
- Other types of failure will be dealt with in other ways
- Log
- 就是紀錄做過的動作
- 紀錄在?
- cache
- failure時可能會消失
- log file
- failure後依然存在
- 只要有就是真的做過!!
- failure後依然存在
- cache
- 動作有?
- 操作
- 實際上的操作 with tx id
- 改值、table等等
- mark
- tx 開始、commit
- rollback
- 實際上的操作 with tx id
- 操作
- 目的是?
- Recovery: Rollback未完成/已完成的tx
- 未完成的tx: 在log file
- Rollback: 把tx取消掉
- 動作
- 從尾開始
- undo對到tx id的item
- 直到遇到tx id的start
- 動作
- Recovery: Rollback未完成/已完成的tx
- 紀錄在?
- Checkpoint
- 幫log分界,不然每次都跑整條其實很慢
- Checkpoint之前的commit可以不用管!!
- Quiescent Checkpointing
- 動作
- 關tx
- 等現在正在跑的tx好 (可能很久)
- flush all buffer
- 把checkpoint寫到log cache,再到log file
- 開tx

- 動作
- Nonquiescent Checkpointing
- 動作
- 關tx
- 在checkpoint的log中記錄現在正在跑的tx的tx id
- flush all buffer
- 把checkpoint寫到log cache,再到log file
- 開tx

- 動作
- 幫log分界,不然每次都跑整條其實很慢
- 就是紀錄做過的動作
- 怎麼Recovery
- Undo-only Recovery
- Log有
- commit
- flush改完的block
- 塞commit log到buffer
- 塞到log file
- rollback
- flush改完的block
- 塞commit log到buffer
- 塞到log file
- commit
- 動作
- 從尾到頭,看每個item
- 紀錄commit、rollback的tx id
- 做完的
- 實際上的操作
- tx id有看過?
- 沒事
- 沒看過?
- undo
- tx id有看過?
- 紀錄commit、rollback的tx id
- 從尾到頭,看每個item
- Log有
- UNDO-REDO recovery 1
- Log有
- commit
flush改完的block- 塞commit log到buffer
- 塞到log file
- rollback
- flush改完的block
- 塞commit log到buffer
- 塞到log file
- commit
- 動作
- UNDO (消除uncommit的影響)
- 從尾到頭,看每個item
- 紀錄commit、rollback的tx id
- 做完的
- 實際上的操作
- tx id有看過?
- 沒事
- 沒看過?
- undo
- tx id有看過?
- 紀錄commit、rollback的tx id
- 從尾到頭,看每個item
- REDO (讓commit保證存在)
- 從頭到尾,看每個item
- 在commit list的item
- redo
- 在commit list的item
- 從頭到尾,看每個item
- 動作重複做沒關係嗎?
- 都是set value,沒差,反正順序對
- idempotent
- 都是set value,沒差,反正順序對
- UNDO (消除uncommit的影響)
- Log有
- UNDO-REDO recovery 2
- Log有
- commit
flush改完的block- 塞commit log到buffer
- 塞到log file
- rollback
flush改完的block- 塞commit log到buffer
- 塞到log file
- commit
- 動作
- UNDO (消除uncommit的影響)
- 從尾到頭,看每個item
- 紀錄commit、
rollback的tx id- 做完的
- 實際上的操作
- tx id有看過?
- 沒事
- 沒看過?
- undo
- tx id有看過?
- 紀錄commit、
- 從尾到頭,看每個item
- REDO (讓commit保證存在)
- 從頭到尾,看每個item
- 在commit list的item
- redo
- 在commit list的item
- 從頭到尾,看每個item
- 動作重複做沒關係嗎?
- 都是set value,沒差,反正順序對
- idempotent
- 都是set value,沒差,反正順序對
- UNDO (消除uncommit的影響)
- Log有
- Redo-Only Recovery
- steal
- tx中改過的block可能在commit完成前就被swap出去!!
- 如果沒有steal
- 只要redo就好
- 因為會到log file的state與HDD的一定一致
- 只要redo就好
- steal
- Repeating history
- Early Lock Release
- meta-structrue的lock會提早釋放 (但block不釋放lock)
- 不然要操作其他block時無法concurrent
- 變成要等meta-struct
- 不然要操作其他block時無法concurrent
- 變成block與meta的更新會不一致!!
- Logical Operations
- 不能根據當時的state做直接的undo
- state可能被其他tx變了,雖然block有lock,但meta沒有!!
- 這也代表undo不是idempotent
- undo也是屬於一般的動作了
- 也要記到log
- undo也是屬於一般的動作了
- 不能根據當時的state做直接的undo
- Logical Operations
- meta-structrue的lock會提早釋放 (但block不釋放lock)
- Rollback Logical Operations (soft delete)

- 卡在中間?
- 把剩下的直接undo
- 跑完了?
- 先拿要拿的所有lock
- 再undo
- 卡在中間?
- Recovery by Repeating History
- REDO (重建現場)
- 從最近的checkpoint,開始重作所有動作
- UNDO (消去未完成tx的影響)
- 看REDO-UNDO recovery
- Logical OPs怎麼處理?
- 卡在中間?
- 把剩下的直接undo
- 跑完了?
- skip (soft delete)
- 卡在中間?
- 原本現在連undo都要log,所以有另一個名字
- Compensation Logs
- REDO (重建現場)
- Early Lock Release
- Undo-only Recovery
- Physiological logging (op reorder你敢信)
- 把一些OPs集中成一個Logical Operation
- 可以省log大小
- 但原本執行上的dependency沒了
- 不能直接REDO
- REDO-UNDO Recovery in Physiological logging
- REDO (重建現場)
- 跳過已經redo過的Physiological logging
- how?
- skip, in ARIES algorithm
- how?
- 跳過已經redo過的Physiological logging
- UNDO (消去未完成tx的影響)
- 把Physiological logging當成一個op去undo
- REDO (重建現場)
- 把一些OPs集中成一個Logical Operation
- 定義Failure
- Concurrency
Query engine
- 把SQL compile 成 AST (relational algebra)
- relational algebra
- relational algebra
- 做plan(選tree的樣子,做cost estimation)
cost estimation
定義cost
- number of block accesses: 掃到多少block
B(p)- 有多少record被output:
R(p) - 在p table中的f field的值域大小:
V(p,f) - index的成本:
SearchCost(p,f) 
- 有多少record被output:
- number of block accesses: 掃到多少block
跑跑看

- R(student)=10000
- B(student)=1000
- B(dept)= 500
- selectivity(s-id=5&major-id=4)=0.01
- Left: (1000+10000*500)*10ms = 13.9 hours
- Right: (1000+100000.01500)*10ms = 8.4 mins
estimate this cost

- 值域很大,不可能1對1的去看
- 分區!!

- 怎麼算、怎麼實作 skip (見 Query Optimization)
Generate trees
- Not finding the best tree
- Avoiding bad trees!!
- consider left-skew candidate trees only
- 在join時,大部分都是走訪右邊

- Goal
↓B(root)reduced to↓R(c1)- Pushing Select ops down
- 越早select越好

- Greedy Join ordering

- 只要確保每次join是最小,最後就是最小 (DP)
- Selinger-Style Optimizer
- Selinger-Style Optimizer
- Pushing Select ops down
- Goal
- Not finding the best tree
Deterministic Query Planning Algorithm
從from拉table
跑where
再跑select
- group by, having?
- group by, having?
一直return回去
- 用scan去爬每一個node的record
- Pipelined Scanning
- call一次給一筆
- Materialized Scanning
- batch處理,放到temp file,一次回傳
- Pipelined Scanning
- 丟給上一層做下一步處理
Storage engine
怎麼被存的? (實作OS的hdd與mem管理)
- Database: directory
- Table: file
- Record: bytes
怎麼與HDD互動? (實作可以跑query的file system)


- BlockId
- Immutable
- Identifies a specific logical block
- A file name + logical block number
BlockId blk = new BlockId("std.tbl", 23);
- Page
- Holds the contents of a block
- Backed by an I/O buffer in OS
- Not tied to a specific block
- Read/write/append an entire block a time
- Set values are not flushed until write()
- Holds the contents of a block
- BlockId
- 怎麼增加從disk拉的速度? 兩個方向
- low-level block API
- Pros
- 可以直接控制phy層資料的位置
- 不用管OS的任何限制
- Cons
- 實作十份複雜
- 沒有portability
- Pros
- file system
- Pros
- 簡單易用
- Cons
- 無法控制phy層資料的位置
- 無法控制page
- filesystem的實作可能把db的正確性破壞掉
- 只能一直flush
- Pros

- low-level block API
怎麼與mem互動? (實作block的cache)

- cache什麼?
- user data (DBs, including catalogs)
- logs (meta-writes)
- cache什麼?
- No Virtual Memory!!
- bad page replacement algorithms
- OS可能換到不想要的page
- uncontrolled delayed writes
- Swapping 無法控制 (should be direct I/O!!)
- 需要swap的page資訊(meta data)
- bad page replacement algorithms
- Self-Managed Page
- Controlled swapping
- Supports meta-writes
- Cache Pages
- Access Pattern
- Random block reads and writes
- Concurrent access to multiple blocks
- Predictable access to certain blocks
- how to cache?
- buffer pool: a pool of pages
- Caching multiple blocks
- Implement swapping
- Pool Size
- 要夠大 (至少所有正在用到的page都要放到pool)
- 不然會Deadlock
- detect deadlock
- 看pin有沒有timeout
- deal with deadlock
- 抓一個犧牲者
- 把他的block全部unpin
- 之後在慢慢pin回來
- 抓一個犧牲者
- 如果是一個人pin爆了pool?
- 只能死亡 (丟例外)
- detect deadlock
- 不然會Deadlock
- 要夠大 (至少所有正在用到的page都要放到pool)
- 利用Predictable access block
- Pinning Blocks: 不會被swap出去
- 流程
- pin block 在某個page
- read
- 完成就unpin block
- A block can be pinned multiple times
- 流程
- Pinning Pages:
- Hit
- cache成功
- Swapping
- page dirty要swap回去
- 很多page? replacement strategies
- Waiting
- 所有人都pin了,所以要等
- Hit
- Buffers = page + page的meta data
- Pinning Blocks: 不會被swap出去
- 例子



- 現在做
pin(60); pin(70);
- Buffer Replacement Strategies
- Naïve
- 只要unpin的就好
- hit rate低
- buffers are not evenly utilized
- 只要unpin的就好
- FIFO
- 挑read in時間最早的
- Assumption: the older blocks are less likely to be used in the future
- counter: catalog blocks!!
- 挑read in時間最早的
- LRU
- 找最早unpin的
- Assumption: blocks that are not used in the near past will unlikely be used in the near future
- 找最早unpin的
- Clock
- 很像Naïve,但是從上次replace的地方開始找
- 很像Naïve,但是從上次replace的地方開始找
- Naïve
- buffer pool: a pool of pages
- Access Pattern
- Caching Logs
- Log用在
- ACID的C與I,Write-Ahead-Logging (WAL)
- commit時
- log在tx中做的動作到buffer
- 要commit時,先把buffer倒到log file
- 倒完再寫一個完成commit(COMMIT log)的log到log file
- swap page時
- 把buffer flush掉
- rollback
- 誰要rollback?
- 沒有COMMIT log的tx
- 3 possibilities for each action on disk
- With log and block
- 用log去undo,把block改好
- With log, but without block
- 用log去undo,把block改好
- Without log and block
- 不用管
- With log and block
- 誰要rollback?
- Assumption of WAL
- each block-write either succeeds or fails entirely on a disk, despite power failure
- commit時
- ACID的C與I,Write-Ahead-Logging (WAL)
- 需要Pool嗎?
- 不用
- log是single buffer
- Always appends
- Always sequential backward reads
- 不用
- Log用在
record怎麼存? (linux的fs只有char與block,但現在我們有datatype)
所有record(a table)都要在同一個file?
- Homogeneous
- 有利於single-table queries
- Heterogeneous
- 有利於需要join的queries
- Homogeneous
一筆record(row)的所有部分都要在同一個block?
- Spanned

- 沒有空間浪費
- record大小不用受制於block大小
- Unspanned

- 只要讀一個block就是一筆record
- Spanned
所有部分都要緊貼著彼此嗎?
- Row-oriented store
- Row-by-row

- Column-oriented store
- 存成好幾個array

- Pros & Cons
- Row-oriented store
欄位(datatype)要固定大小嗎?
- Fixed-Length
- Variable-Length



- 內部block怎麼處理
- the record’s length changes
- delete a record
- soft delete

- 刪掉的空間沒辦法用
- 把space空出來
- soft delete
- cannot random access a record in a page => no position information
- page layout
- header放
- record總數
- free space的終點
- 指到record的mapping table

- 改大小的話
- 要重新找連續的free space
- 碎片化
- VACUUM command
- header放
- page layout
- the record’s length changes
怎麼管理free space (怎麼知道哪裡有free space)
- Chaining
- Meta-Pages
- Meta-File
- Chaining
每個record的大小? 其他與db有關的訊息放在哪?
- catalog tables
- Table metadata
- table的資訊 (大小、長度…)
- View metadata
- view的訊息 (creater,…)
- Index metadata
- 每個欄位的index
- Table metadata
- in mem
- Statistical metadata
- 關於table的統計資訊,可以在plan時使用
- Statistical metadata
- catalog tables
Group Communication
DB Workloads
- Operational workloads
- OLTP (On-line Transaction Processing)
- 跑tx多,執行時間短
- Analytic workloads
- Online (OLAP) or offline
- 資料分析


Cloud DB
SAE
high Scalability
- 可水平擴展來拉throughput
- S through partitioning
- Partition your hot tables

- horizontally
- vertically
- 要處理

- 分散的
- metadata manager
- query processor (record, plan)
- transactions
- Distributed S2PL
- 看 分散式那一份筆記 的 怎麼commit那一部分
- Distributed S2PL
- Partition your hot tables
- S through partitioning
- 可水平擴展來拉throughput
high Availability
- 不能死,除了網路、硬體問題外
- A through replication
- Replicate all tables across servers

- Replication
- Eager
- 在ㄌtx commit之前,每台都要完成
- strong consistency, slow tx

- 在ㄌtx commit之前,每台都要完成
- Lazy
- local先寫,之後再非同步的同步到另一台去
- eventual consistency, fast tx

- local先寫,之後再非同步的同步到另一台去
- Eager
- Who Writes?
- Master/Slave
- write只有某一台處理
- read由其他台負責
- Multi-Master
- write每一台都可以負責
- Master/Slave

- Replicate all tables across servers
- A through replication
- 不能死,除了網路、硬體問題外
Elasticity
- 能根據machine與workload去動態調整data分布
- Re-Partitioning
- Data chunking
- 使用者指定
- 系統生成 (consistent hashing)
- Master server for load monitoring
- Data chunking
- Migrate
- Migration with Determinism
- 做一個空的replica
- 在兩個db上跑同一個tx,只拉用到的data (Foreground Pushing)
- 剩下就是非同步的推 (Background Pushing)
- Migration vs. Crabbing
- Client served by any node running faster
- Migration delay imperceptible
- 我同時serve,我同時migrate

- Migration with Determinism
- Re-Partitioning
- 能根據machine與workload去動態調整data分布
SAE + 完整的retional DB基本上不可能
- Workarounds
- No expressive model
- 在應用層處理(dirty work)
- No flexible queries
- 多發幾個query或是繼續在應用層處理(dirty work)
- No tx and ACID
- 在應用層處理
- No expressive model




















